無料ダウンロード nor flash memory pdf 112842-Nor and nand flash memory pdf
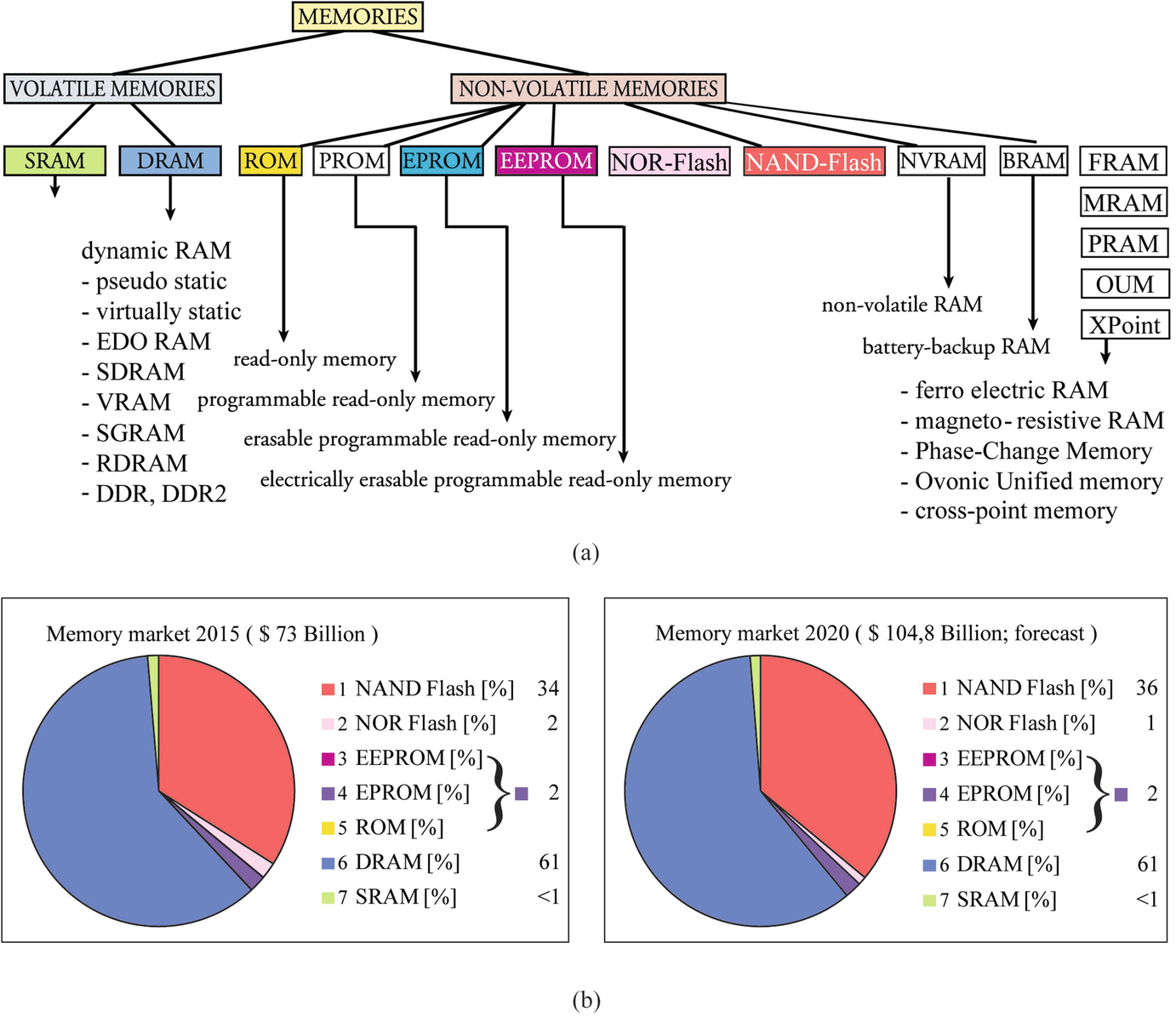
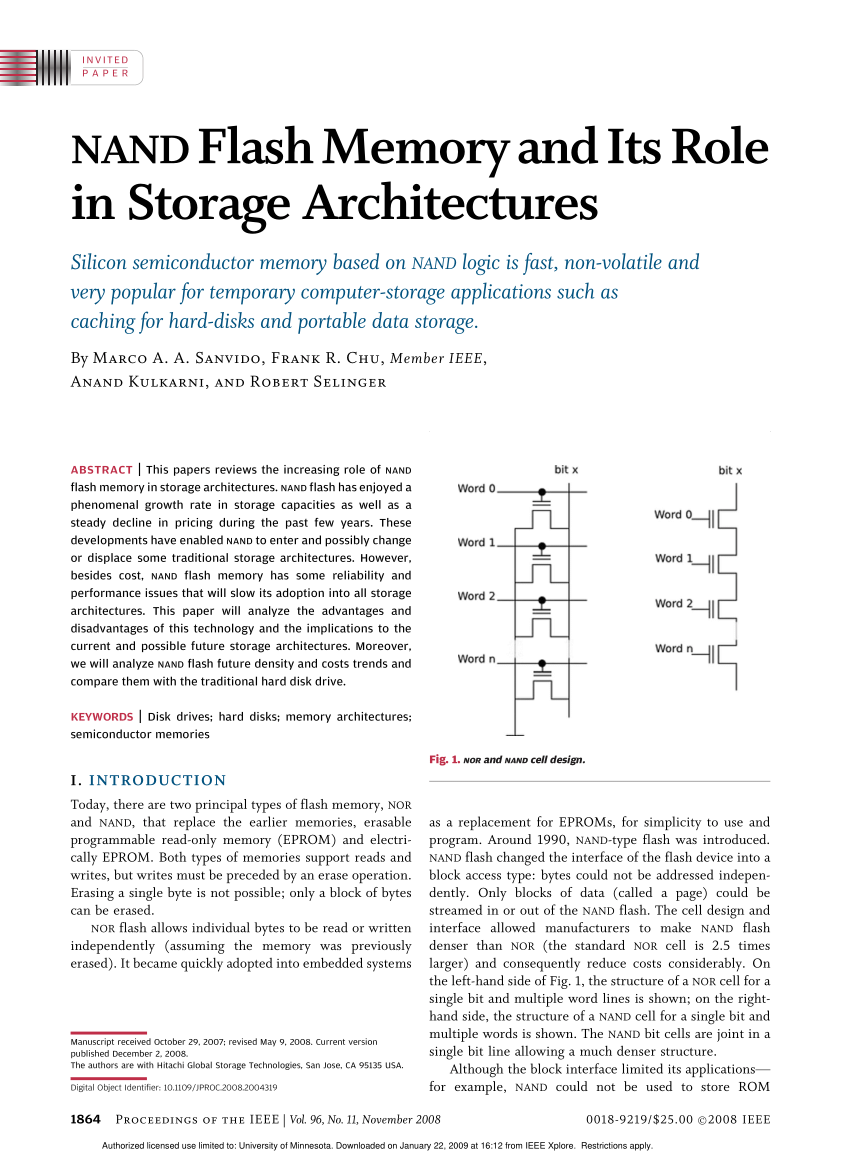
211 Flash Memory Flash memory was invented by DrFujio Masuoka in 1980 at ToshibaFlash memory can be divided into NOR and NANDbased memory 21 NORbased flash memory provides high read performance and enables full address and data bus access Thus, it supports eXecution In Place (XIP), which allows applications to run directly from the flash memory instead32Mb, 64Mb, 128Mb 3V Embedded Parallel NOR Flash Features PDF aef84dc44a7 m29ew_32Mb128Mbpdf Rev B 11/12 EN 1 Micron Technology, Inc reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice Table 7 32Mb Memory Map · 3 Two Technologies Compared NOR vs NAND, Rev 11 91SR0148L INTRODUCTION Two main technologies dominate the nonvolatile flash memory market today NOR and NAND NOR flash was first introduced by Intel in 19, revolutionizing a market that was then dominated by EPROM and EEPROM devices NAND flash architecture was introduced by
Code Storage Flash Memory 1 2v Serial Nor Flash Winbond Lower Power Flash
Nor and nand flash memory pdf
Nor and nand flash memory pdf-NOR flash is basically a random access memory device Is has enough address pins to map its entire media, allowing for easy access to each and every one of its bytes NAND devices are interfaced serially via a rather complicated I/O interface, which may vary from one device to another or from vendor to vendorMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QL02GCBB Features • Stacked device (four 512Mb die) • SPIcompatible serial bus interface • Single and double transfer rate (STR/DTR) • Clock frequency – 133 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in STR – 90 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in DTR



Code Storage Flash Memory 1 2v Serial Nor Flash Winbond Lower Power Flash
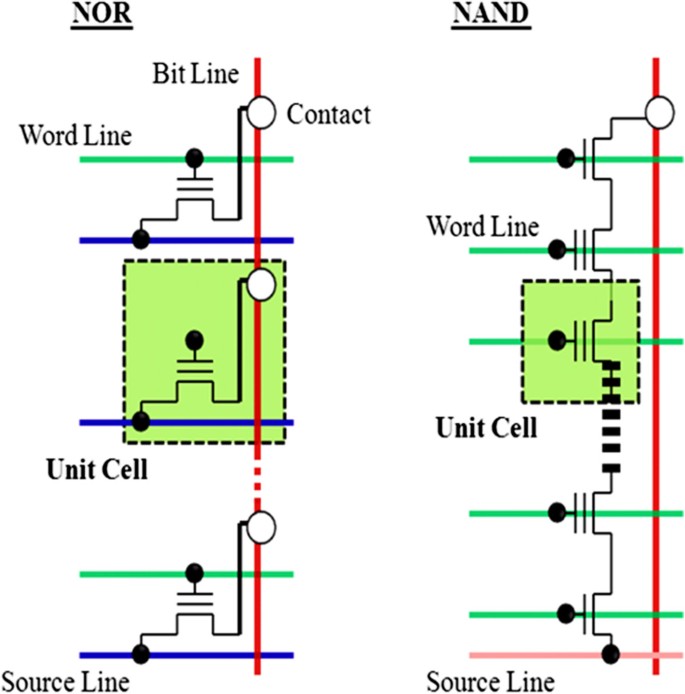
Hynix Develops 26nm NAND Flash Memory Tuesday, February 09, 10 South Korea's Hynix Semiconductor Inc, the world's secondlargest memory chipmaker, said Tuesday that it has developed a 26nanometer based NAND flash memory chip The company is the world's second flash memory maker to apply the below 30nanometer technology · NAND and NOR Flash Memory Architecture In the internal circuit configuration of NOR Flash, the individual memory cells are connected in parallel, which enables the device to achieve random access This configuration enables the short read times required for the random access of microprocessor instructions NOR Flash isNAND Flash Memory Block Diagram Page 16Byte 8 b i t 512Byte 32page/Block Redundant Cell Array Register Cell Array Bit Line Basic unit WL1 WL2 WL3 WL4 (WL30) (WL31) (WL32) SG (S) SG (D) ~~ ~~ (Byte) ex256Mb NAND Flash Memory 256Mb NAND Flash Page Size Bytes Block Size 16KBytes # of Blocks 48 Blocks
Introducing the latest in memory technology with Semper™ NOR Flash When it comes to automotive technology, your design needs to work the first time, every tThe W25N01GV 1Gbit memory array is organized into 65,536 programmable pages of 2,048bytes each The entire page can be programmed at one time using the data from the 2,048Byte internal buffer Pages can be erased in groups of 64 (128KB block erase) The W25N01GV has 1,024 erasable blocks W25M321AV consists of •OctaBus Memory provides extendable I/O capability to broaden our Serial NOR Flash throughput efficiently It dedicates to raising the product performance with the fastest 0MHz frequency, combining with the DTR feature More
NOR Flash memories typically are specified to withstand 100K P/E cycles without suffering read/program/erase functional failures (please confirm with applicable flash datasheet) Data retention can be defined as the capability of retaining stored information over time Similarly, Data retention Time is the period of time the memory can retain data · NOR Flash, on the other hand, are shipped with zero bad blocks with very low bad block accumulation during the life span of the memory Thus, when it comes to the reliability of stored data, NOR Flash has an advantage over NAND Flash Another aspect of reliability is data retention, where NOR Flash again holds an advantageHowever, many of the scaling con



What Is The Difference Between Nand And Nor Flash Edn



Pdf Introduction To Flash Memory Semantic Scholar
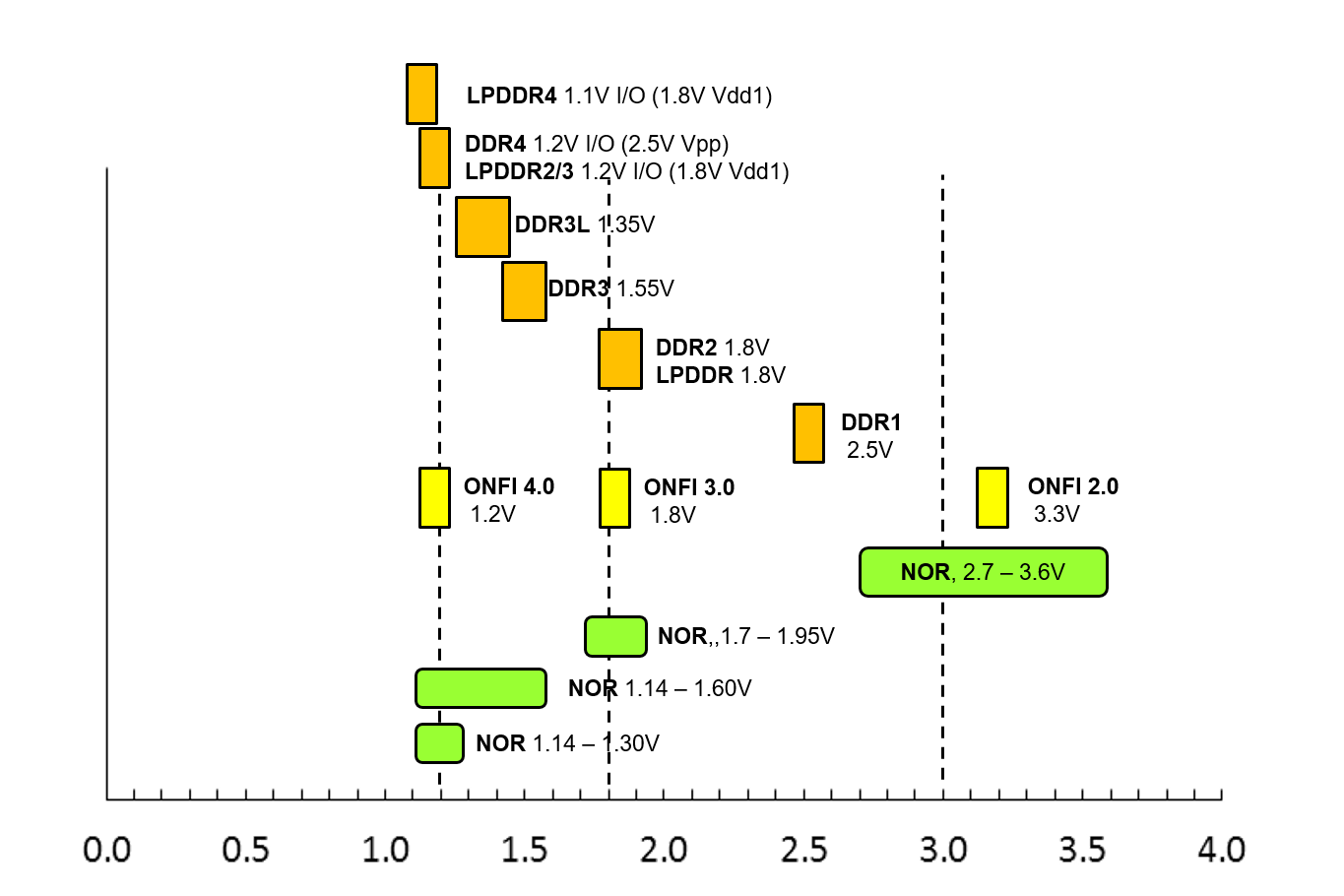
Applied voltage Flash memory is categorized into two basic approaches NOR flash, characterized by a fast initial access time for high read performance;2603 · NOR flash memory use cases NAND flash is typically used for data storage and NOR flash is deployed as an embedded device for code execution NOR flash is used for industrial robotics, medical devices, scientific instruments, IoT devices or portable consumer products such as cameras, wearables or mobile phonesMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q064A13E1240x, N25Q064A13EF640x, N25Q064A13EF840x, 64Mb, 3V, Multiple I/O Serial Flash Memory Features PDF aeff4 n25q_64mb_3v_65nmpdf Rev I 10/12 EN 4 Micron Technology, Inc reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice



Pdf Fpga Implementation Of Nor Flash Storage Controller Ijesrt Journal Academia Edu



Pdf Overview Of Emerging Non Volatile Memory Technologies
16bit NOR Flash memory 21 FSMC configuration To control a NOR Flash memory, the FSMC provides the following possible features Select the bank to be used to map the NOR Flash memory there are 4 independent banks which can be used to interface with NOR Flash/SRAM/PSRAM memories, each bank has a separate Chip Select pinRecently we have manufactured NORtype flash EEPROM memories and observed a data loss in memory cells during backend device screening procedures using high temperature retention bakeThe Semper™ NOR Flash Memory Family is Cypress' newest highperformance, safe, and reliable NOR Flash memory solution that integrates critical safety features for automotive and industrial systems With Semper Flash, Cypress introduces the industry's ˜rst ASILB Compliant and ASILD Ready NOR Flash Memory


Tyadgb Pdf Datasheet Download Ic On Line



Pdf Vhdl Implementation Of Nor Flash Controller Srin Ankal Academia Edu
FLASH Programming Problems, page 9 (flash_diagnosispdf) bus error There is no memory at the address range declared for the FLASH Please check the bus configuration for the FLASH device Refer to "Checking the Bus Configuration" in Tips to Solve NOR FLASH Programming Problems, page 49 (flash_diagnosispdf) for details data alignment error Wrong or incorrect alignment used while writing the FLASHNOR Flash Memory Erase Operation November 19 wwwadestotechcom By Csaba Moldvai Applications Engineering NOR Flash Memory Erase Operation Page 2 of 22 3600 Peterson Way, Santa Clara CA , USA •Phone 1 (408) • email info@adestotechcomAnd NAND flash, characterized by a slow initial access time and high write performance This article will focus on the scaling of NOR flash memory;



Flash Memory Wikipedia



Nor Nand Flash Guide Pdf Flash Memory Solid State Drive
Parallel NOR Flash Embedded Memory JS28F256M29EWxx, PC28F256M29EWxx, RC28F256M29EWxx JS28F512M29EWxx, PC28F512M29EWxx, RC28F512M29EWxx JS28F00AM29EWxx, PC28F00AM29EWxx, RC28F00AM29EWxx PC28F00BM29EWxx, RC28F00BM29EWxx Features • 2Gb = stacked device (two 1Gb die) • Supply voltage – VCC =SPI NOR Flash Key Features Available in 18V, 25V, 30V and wide voltage ranges Operates in Single, Dual and Quad I/O SPI modes QuadSPI data transfer of up to 532Mb/s outperforms many asynchronous parallel Flash memories Flexible memory architecture (sector size 4K bytes, block size 32/64K bytes)Embedded NOR flash memory, show up to 400 MHz operation, 168 POps/J energy efficiency, and 3945 TOps/mm2 computing throughput Moreover, the circuit is robust against processvoltagetemperature variations, in part due to inclusion of additional FG cells that are utilized for offset compensation1 KEYWORDS



Non Volatile Memory Flash Memory Computer Data Storage


Overview Of Emerging Nonvolatile Memory Technologies Springerlink
NOR Flash Memory Controller with WISHBONE Interface Documentation FPGARD096 12 1/22/21 PDF 16 MB NOR Flash Memory Controller with WISHBONE Interface Source Code RD1087 11 11/8/10 ZIP 1981 KBSPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) NAND Flash provides an ultra costeffective while high density nonvolatile memory storage solutionfor embedded systems, based on an industrystandard NAND Flash memory coreis an attractive It alternative to SPINOR and standard parallel NAND Flash, with advanced featuresNm NOR flash memory Each array performs a very fast and energyefficient analog vectorbymatrix multiplication, which is the bottleneck for signal propagation in neuromorphic networks All functional components of the prototype circuit, including 2 synaptic arrays with 101,780 floatinggate synaptic cells, 74 analog neurons, and the


K5a3280yba Pdf Datasheet Download Ic On Line


2 1 1 Flash Memory
This is more than four times the performance of ordinary Serial Flash (50MHz) and even surpasses asynchronous Parallel Flash memories while using fewer pins and less space Faster transfer rates mean controllers can execute code (XIP) directly from the SPI interface or further improve boot time when shadowing code to RAMParticularly the flash memory process induces more and more complex faults in such memories Table 1 Comparison of NAND and NOR Flash Memories NAND NOR Sequential READ access Random READ access Fast PROGRAM Slow PROGRAM Fast ERASE Slow ERASE Fig 1 NAND and NOR Flash Structures128Mb 3V Embedded Parallel NOR Flash Features PDF aefc m29dw_128gpdf Rev B 02/16 EN 3 Micron Technology, Inc reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice 12 Micron Technology, Inc All rights reserved Downloaded from Arrowcom



Code Storage Flash Memory Serial Nor Flash Winbond



Pdf Architectures And Optimization Methods Of Flash Memory Based Storage Systems
ISSCC 17 / SESSION 11 / NONVOLATILE MEMORY SOLUTIONS / 112 112 A 1Mb Embedded NOR Flash Memory with 39μW Program Power for mmScale HighTemperature Sensor Nodes Qing Dong1, Yejoong Kim1, Inhee Lee1, Myungjoon Choi1, Ziyun Li1, Jingcheng Wang1, Kaiyuan Yang1, YenPo Chen1, Junjie Dong1,84 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLIDSTATE CIRCUITS, VOL 37, NO 1, JANUARY 02 Circuit Techniques for a 18VOnlyNAND Flash Memory Toru Tanzawa, Tomoharu Tanaka, Ken Takeuchi, and Hiroshi Nakamura Abstract— Focusing on internal highvoltage ( ) switching and generation for lowvoltageNAND flash memories, this paperPDF This paper mainly focuses on the development of the NOR flash memory technology, with the aim of describing both the basic functionality of the



Study Of Bad Block Management And Wear Leveling In Nand Flash Memories Pdf Document



Flyer Nor Nand Flash Guide Flash Memory Solid State Drive
Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory 18V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q128A Features • SPIcompatible serial bus interface • 108 MHz (MAX) clock frequency • 17–V single supply voltage • Dual/quad I/O instruction provides increased throughput up to 432 MHz • Supported protocols – Extended SPI, dual I/O, and quad I/OMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL128ABA Features • SPIcompatible serial bus interface • Single and double transfer rate (STR/DTR) • Clock frequency – 133 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in STR – 90 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in DTR • Dual/quad I/O commands for increased throughput up to 90 MB/sMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory 18V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase MT25QU512ABB Features • SPIcompatible serial bus interface • Single and double transfer rate (STR/DTR) • Clock frequency – 166 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in STR – 90 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in DTR • Dual/quad I/O commands for increased throughput up to 90 MB/s



Flash Memory Wikipedia



Micron Serial Nor Flash Memory Pdf Free Download
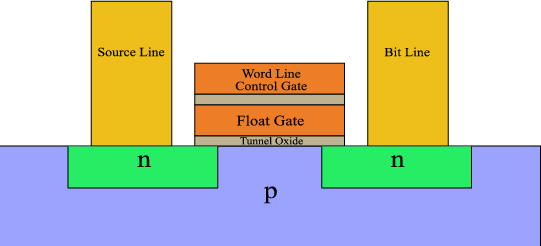
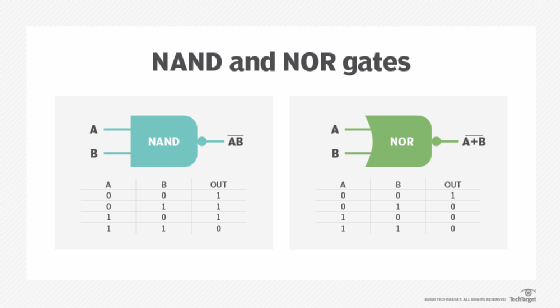
Flash memory is an electronic nonvolatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates NAND flash and NOR flash use the same cell design, consisting of floating gate MOSFETsMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB, Sector Erase MT25QL256ABA Features • SPIcompatible serial bus interface • Single and double transfer rate (STR/DTR) • Clock frequency – 133 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in STR – 90 MHz (MAX) for all protocols in DTR • Dual/quad I/O commands for increased throughput up to 90 MB/sMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB, 32KB, 64KB Sector Erase Enhanced Program and Erase Speed N25Q064A13ExxDxx Features • SPIcompatible serial bus interface • 108 MHz (MAX) clock frequency • 27–36V single supply voltage • Dual/quad I/O instruction provides increased throughput up to 432 MHz • Supported protocols


Semiconductor Memory Market Forecast 26 Global Share Report



Code Storage Flash Memory 1 2v Serial Nor Flash Winbond Lower Power Flash
Onchip/NOR FLASH Programming User's Guide 10 ©19 Lauterbach GmbH Offchip FLASH Devices Supporting CFI Here we focus on programming of CFIconform FLASH devices, since most NOR FLASHs support this standard CFI stands for Common Flash memory Interface It is an open standard that describes how selfidentifying1412 · NOR Flash Memory Family Decoder 1214 S 25 H S 512 T Technology J = 110nm Floating Gate (FG) N = 110nm MirrorBit® (MB) K = 90nm FG P = 90nm MB L = 65nm FG R, S = 65nm MB T = 45nm MB Density 008 = 8Mb 064 = 64Mb 512 = 512Mb 04G = 4Gb 016 = 16Mb 128 = 128Mb 01G = 1Gb 032 = 32Mb 256 = 256Mb 02G = 2Gb Voltage D = 25 V L = 30 V S =2812 · NOR flash memory is one of two types of nonvolatile storage technologies NAND is the other Nonvolatile memory doesn't require power to retain data NOR and NAND use different logic gates the fundamental building block of digital circuits in each memory



Pdf See And Tid Response Of Spansion 512mb Nor Flash Memory Mingyang Zhang Academia Edu



Pdf Architectures And Optimization Methods Of Flash Memory Based Storage Systems Semantic Scholar
The Micron Parallel NOR Flash memory is the latest generation of Flash memory devices Benefits include more density in less space, highspeed interface device, and support for code and data storage Features include highperformance synchronousburst read mode, fast asynchronous access times, low power, flexible security options, andFlash memory scaling is far behind CMOS logic device scaling For example, the EOT of the gate stack in semiconductor flash memory is still more than 10nm Moreover, semiconductor flash memory still requires operation voltage of more than 10V, while the operation voltage of CMOS logic has been scaled to 1V or even lessFlash memory was developed from EEPROM (electronically erasable programmable readonly memory) It must be erased before it can be rewritten with new data The erase is based on a unit of a block, which varies from 256 KB to MB There are two types of flash memory which dominate the technology and market NOR flash and NAND flash


Code Storage Flash Memory Serial Nor Flash Winbond


Flash Memory Wikipedia
Shows how to boot from internal Flash memory, configure external memories and then jump to user application located on external memory The user can select QSPI/OSPI Flash memory, FMCNOR Flash memory, external SDRAM, external SRAM or external OSPIRAM for code execution ExtMem_Application\LedTogglingDiscussed earlier The remainder of the application note will cover only flash memory 2 Flash Memory Architectures The two main architectures dominate the flash memory they are NOR and NAND NOR is typically used for code storage and execution NOR allows quick random access to any location in the memory array, 100% known good bits for the life of the part, and codeAll these memories use the NOR flash architecture Aphoto of SanDisk's 32Mbit flash cell (used on its CompactFlash cards) featuring a cell size of 18µm2 is shown Figure 107 ARCHITECTURE As with other semiconductors, the flash memory chip size is



Flash Memory An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Flash Memory Market For Pdf By Khistimandar18 Issuu
· The raw state of flash memory cells (A singlelevel NOR flash cell) will be bit 1's, (at default state) because floating gates carry no negative charges Erasing a flashmemory cell (resetting to a logical 1) is achieved by applying a voltage across the source and control gate (word line) The voltage can be in the range of 9V to 12V



Memory Cell Computing Wikipedia



Pdf Microcontroller Trngs Using Perturbed States Of Nor Flash Memory Cells Semantic Scholar
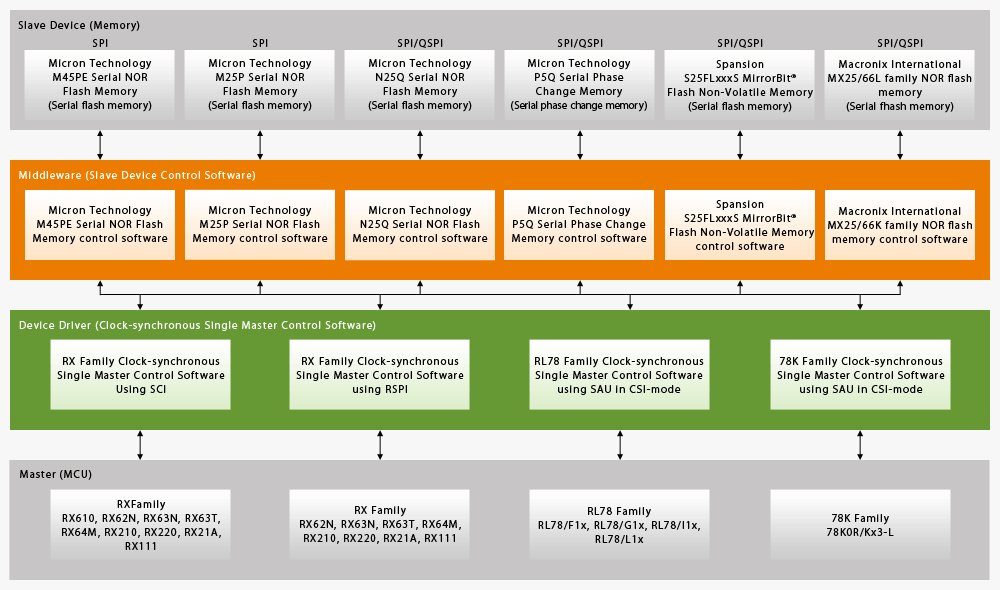


Spi Qspi Serial Flash Memory Qspi Serial Phase Change Memory Driver Renesas
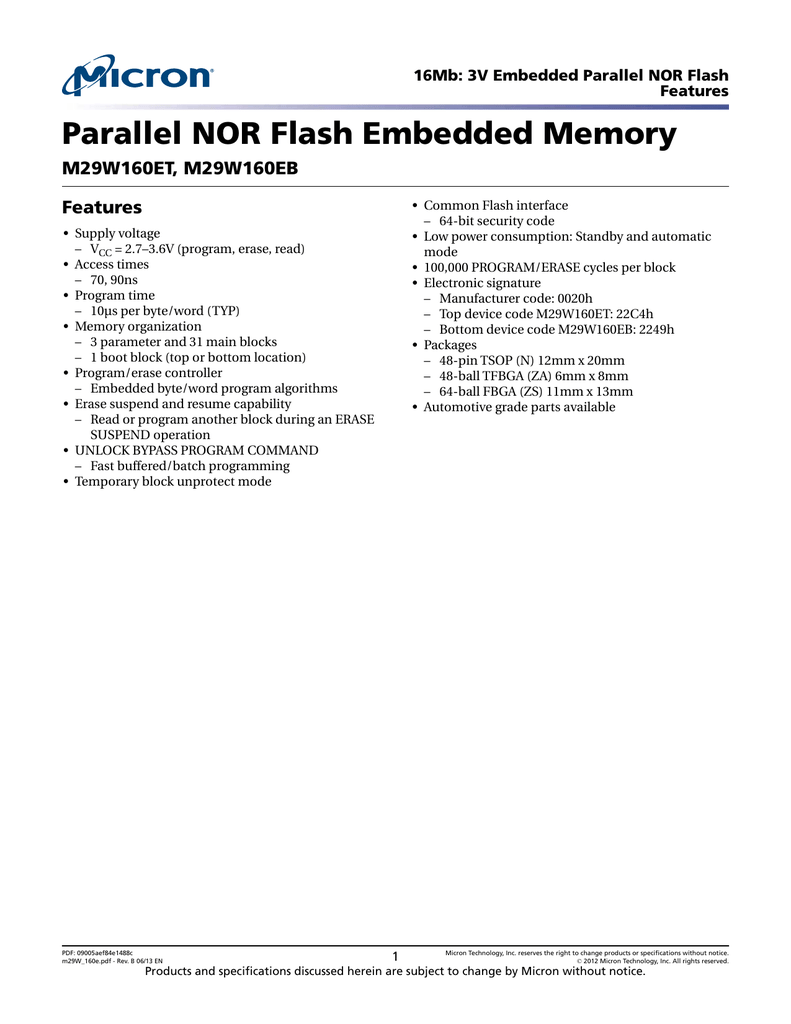


Parallel Nor Flash Embedded Memory M29w160et M29w160eb Features Manualzz



Flash Memory Wikipedia



Nor Flash Memory K8d3x16utc K8d3x16ubc Pdf Document



Pdf Introduction To Flash Memory



Macronix Serial Nor Flash Nonvolatile Memory Solutions


N25q256a Datasheet Pdf Micron Technology



Nand Vs Nor Flash Memory Technology Overview Read Write Erase Speed For Slc Mlc Semiconductor Consulting Expert Pdf Document



K8d1716utc Memory Datasheet Pdf Flash Memory Equivalent Catalog



Slc Nand Kioxia



Pdf A Low Cost Memory Architecture With Nand Xip For Mobile Embedded Systems Bumsoo Kim Academia Edu


What Is Nor Flash Memory And How Is It Different From Nand


Micron Nand Flash Pcb Layout Guidelines Pcb Circuits



Memory Kioxia



Embedded Systems Course Module 16 Flash Memory Basics And Its Interface To A Processor


Js28f256p30tfa Pdf Datasheet Download Ic On Line



Doc Future Proof Flash Memory Anshul Gupta Academia Edu



Flash Memory Keeps Cars Connected



Flash Memory Wikipedia



Code Storage Flash Memory Serial Nor Flash Winbond



Embedded Systems Course Module 16 Flash Memory Basics And Its Interface To A Processor


Ace25q400g Pdf Datasheet Download Ic On Line
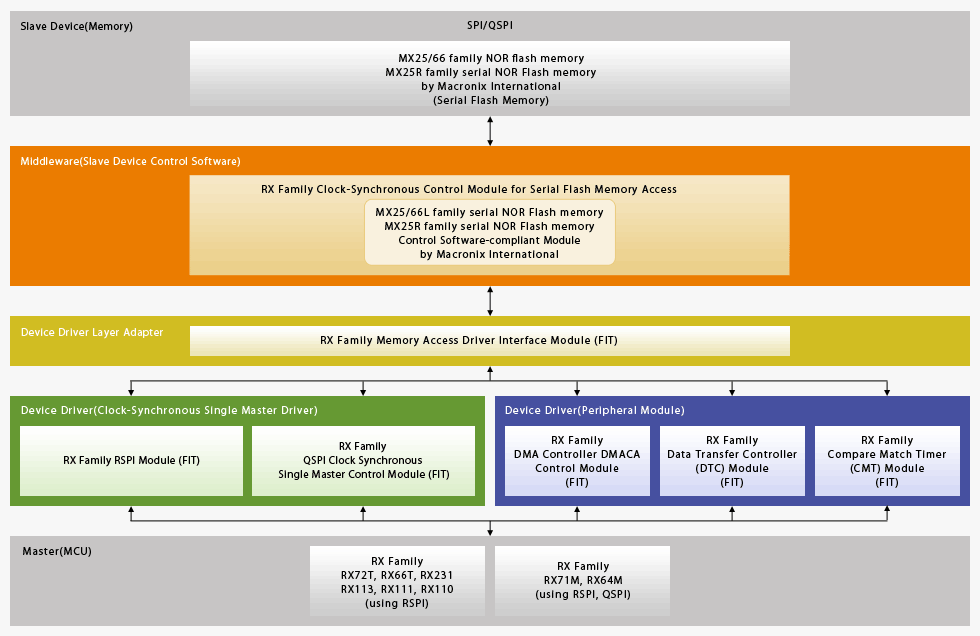


Spi Qspi Serial Flash Memory Qspi Serial Phase Change Memory Driver Renesas
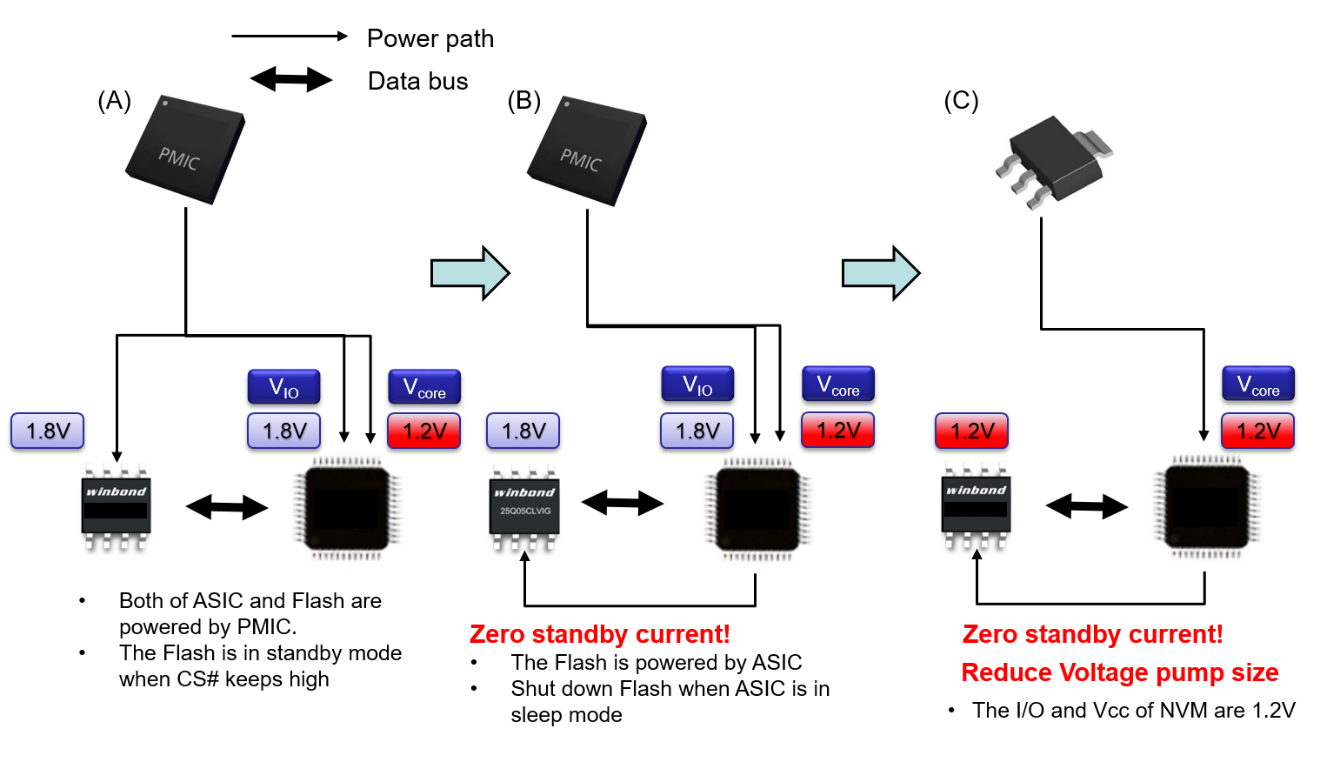


Code Storage Flash Memory 1 2v Serial Nor Flash Winbond Lower Power Flash



S3c2440 Nor Flash Driver 24 Programmer Sought



Nand Vs Nor Flash Types Of Flash Memory


What Is The Difference Between Nand And Nor Flash Memory


N25q256a13e1240 Pdf Datasheet Download Ic On Line



Pdf Flash Memory Cells An Overview



Flash 101 Nand Flash Vs Nor Flash Embedded Com
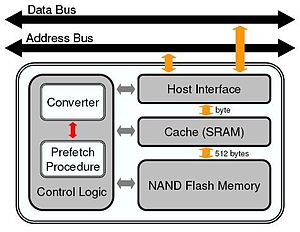


Nor Flash Replacement Wikipedia


Pdf Nand Flash Memory And Its Role In Storage Architectures



Pdf Introduction To Flash Memory



Embedded Systems Course Module 16 Flash Memory Basics And Its Interface To A Processor



Pdf Flashmark Watermarking Of Nor Flash Memories For Counterfeit Detection Semantic Scholar



Micron Nor Flash Datasheet



Flash 101 Nand Flash Vs Nor Flash Embedded Com


N25q256a13esf40 Datasheet Pdf Micron Technology Micron Serial Nor Flash Memory
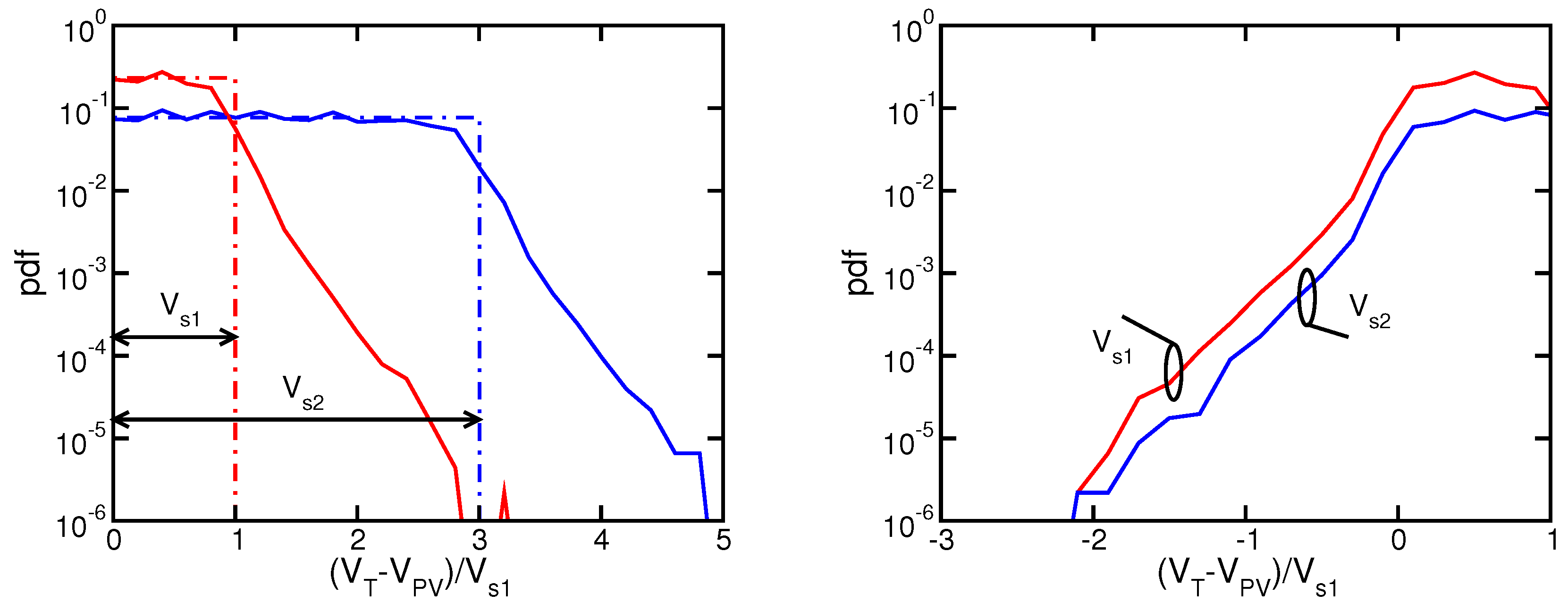


Computers Free Full Text Reliability Of Nand Flash Memories Planar Cells And Emerging Issues In 3d Devices Html



Embedded Systems Course Module 16 Flash Memory Basics And Its Interface To A Processor


N25q00aa Pdf Datasheet Download Ic On Line
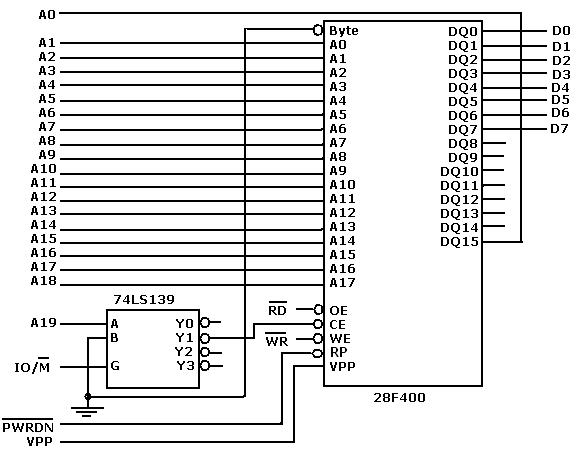


Embedded Systems Course Module 16 Flash Memory Basics And Its Interface To A Processor



Nand Vs Nor Flash Types Of Flash Memory



Micron Serial Nor Flash Memory Pdf Free Download
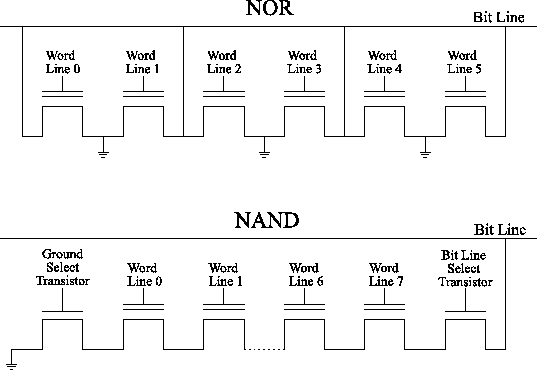


2 1 1 Flash Memory



Pdf Introduction To Flash Memory Semantic Scholar



Pdf An Experimental 1mb 0 11um 4 5f2 1 8volt Multilevel Vertical Split Gate Source Side Injection Test Vehicle For Gigabit Density Nor Flash Memory Loc Hoang Academia Edu



Flash 101 Nand Flash Vs Nor Flash Embedded Com



Micron Nand Flash Pcb Layout Guidelines Pcb Circuits



Flash Storage A Cheat Sheet Techrepublic


コメント
コメントを投稿